Follow Us:
What Is Rotenone
What is rotenone?
Rotenone is an odorless, colorless, crystalline isoflavone used as a broad-spectrum insecticide, piscicide, and pesticide. It occurs naturally in the seeds and stems of several plants, such as the jicama vine plant, and the roots of several members of Fabaceae. It was the first described member of the family of chemical compounds known as rotenoids. Evidence has come to suggest that rotenone may cause Parkinson’s disease to develop from both acute and prolonged exposure.
What is rotenone and how is it typically used
Rotenone (Fig. 50.1A) is a natural compound, used as an insecticide and a herbicide. Rotenone is a naturally occurring complex ketone, derived from the roots of Lonchocarpus species (Uversky, 2004). It is a commonly used pesticide and is also used in lakes and reservoirs to kill fish that are perceived as pests.

What is rotenone compound
Rotenone is a naturally occurring organic heteropentacyclic compound and member of rotenones that is found in the roots of several plant species. It is a mitochondrial NADH:ubiquinone reductase inhibitor, toxin, and metabolite, and is used as an antineoplastic agent and insecticide. It is characterized as a colorless to brownish or a white to brownish-white crystalline solid that is odorless. Exposure occurs by inhalation, ingestion, or contact.
What is rotenone model
Rotenone was first used to model PD in 1985 when Heikkila injected this mitochondrial complex I inhibitor directly into the brain and showed that at a concentration of 5 mM – approximately 500,000-fold higher than its IC50 of 10 nM – it killed dopaminergic neurons2; however, identical results could have been obtained with a high concentration of virtually any toxin, mitochondrial or otherwise. Later, because there was a growing suspicion that PD might be associated with systemic mitochondrial defects, several groups began to experiment with systemic administration of mitochondrial toxins.
What is rotenone classified as
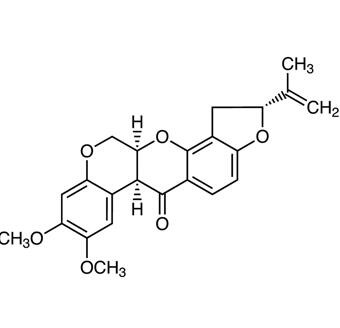
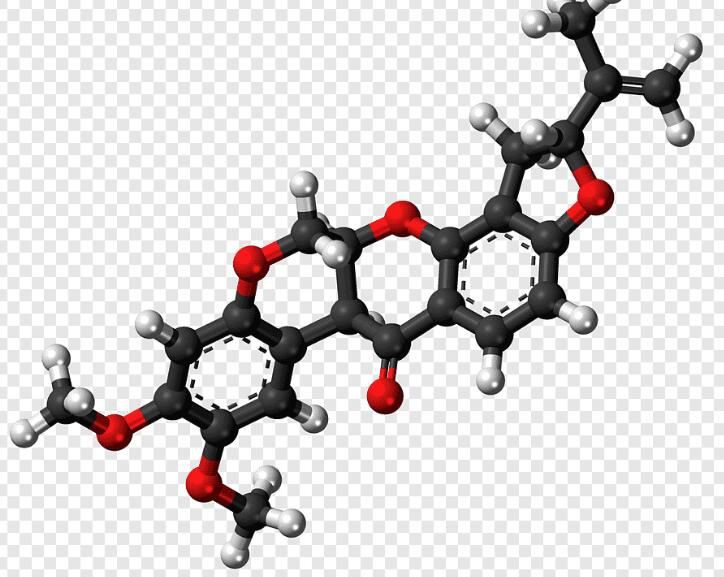
Rotenone is a member of the class of rotenones that consists of 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6(6aH)-one substituted at position 2 by a prop-1-en-2-yl group and at positions 8 and 9 by methoxy groups (the 2R,6aS,12aS-isomer).
Description: Rotenone is a naturally occurring …
Molecular Formula: C23H22O6
Molecular Weight: 394.4
What color is rotenone
It is characterized as a colorless to brownish or a white to brownish-white crystalline solid that is odorless.
What chemical is rotenone
Rotenone is an odorless, colorless, crystalline isoflavone used as a broad-spectrum insecticide, piscicide, and pesticide.
Names
Chemical formula:C23H22O6
Molar mass:394.423 g·mol−1
Appearance:Colorless to red crystalline solid
Odor:odorless
What class is rotenone
Rotenone is a member of the class of rotenones that consists of 1,2,12,12a-tetrahydrochromeno[3,4-b]furo[2,3-h]chromen-6(6aH)-one substituted at position 2 by a prop-1-en-2-yl group and at positions 8 and 9 by methoxy groups (the 2R,6aS,12aS-isomer).
What type of inhibitor is rotenone
Rotenone acts as a strong inhibitor of complex I of the mitochondrial respiratory chain (MRC). The mechanism of action (MOA) comprises inhibition of electron transfer from the iron-sulfur centers in complex I to ubiquinone, leading to a blockade of oxidative phosphorylation with limited synthesis of ATP2.

What is rotenone used for
Rotenone is a natural plant toxin used for centuries by indigenous peoples of Southeast Asia and South America for the harvesting of fish for human con- sumption. It has been used as a commercial insecticide for more than 150 years and for the management of fish populations since the 1930s.
What is the plant that rotenone comes from
Its principal commercial source is the derris plant of the East Indies, but it is also present in a South American plant called ‘cube’ and in the North American plant popularly termed ‘devil’s shoestring’. All the plants that are known to yield rotenone are members of the natural order Legum-inos
For bulk rotenone, please contact us at email: info@greenagribio.com
References:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Rotenone
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/neuroscience/rotenone
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2846992/
https://www.nature.com/articles/srep45465
https://www.doc.govt.nz/documents/science-and-technical/sfc211.pdf


















